Agent Management Guide¶
This guide covers the comprehensive management of KrakenHashes agents, including registration, monitoring, scheduling, and troubleshooting.
Table of Contents¶
- Understanding Agents
- Agent Registration Process
- Managing Agent Connections
- Monitoring Agent Health and Performance
- Agent Scheduling and Availability
- Hardware Capabilities and Benchmarks
- Troubleshooting Agent Issues
Understanding Agents¶
What are Agents?¶
Agents are distributed compute nodes that execute password cracking tasks using hashcat. They connect to the KrakenHashes backend server via WebSocket and receive job assignments based on their availability and capabilities.
Agent Architecture¶
Each agent consists of: - Hardware Detection: Automatic detection of GPUs (NVIDIA, AMD, Intel) and CPUs - Performance Monitoring: Real-time tracking of resource utilization - File Synchronization: Automatic download of wordlists, rules, and hashlists - Job Execution: Running hashcat with specified attack parameters - Result Reporting: Real-time crack updates back to the server
Agent States¶
Agents can be in one of the following states:
pending: Initial registration state, awaiting activationactive: Connected and ready to receive jobsinactive: Disconnected but previously activeerror: Experiencing issues preventing normal operationdisabled: Administratively disabled
Agent Registration Process¶
Overview¶
Agent registration uses a claim code (voucher) system to ensure only authorized agents can join the system.
Creating Claim Codes¶
- Navigate to Admin Panel
-
Go to Settings → Agent Management → Claim Codes
-
Generate New Claim Code
-
Claim Code Types
- Single-use: Can only be used once to register one agent
- Continuous: Can be used multiple times (useful for auto-scaling)
Agent Registration Steps¶
-
Agent Installation
-
Initial Registration
-
Certificate Download
- Agent automatically downloads TLS certificates
-
Stores credentials in
~/.krakenhashes/agent/ -
Connection Establishment
- Agent connects via WebSocket using API key authentication
- Sends hardware information and capabilities
Registration Security¶
- Claim codes are normalized (uppercase, no hyphens)
- API keys are generated using cryptographically secure random bytes
- TLS certificates ensure encrypted communication
- Agent ID and API key must match for authentication
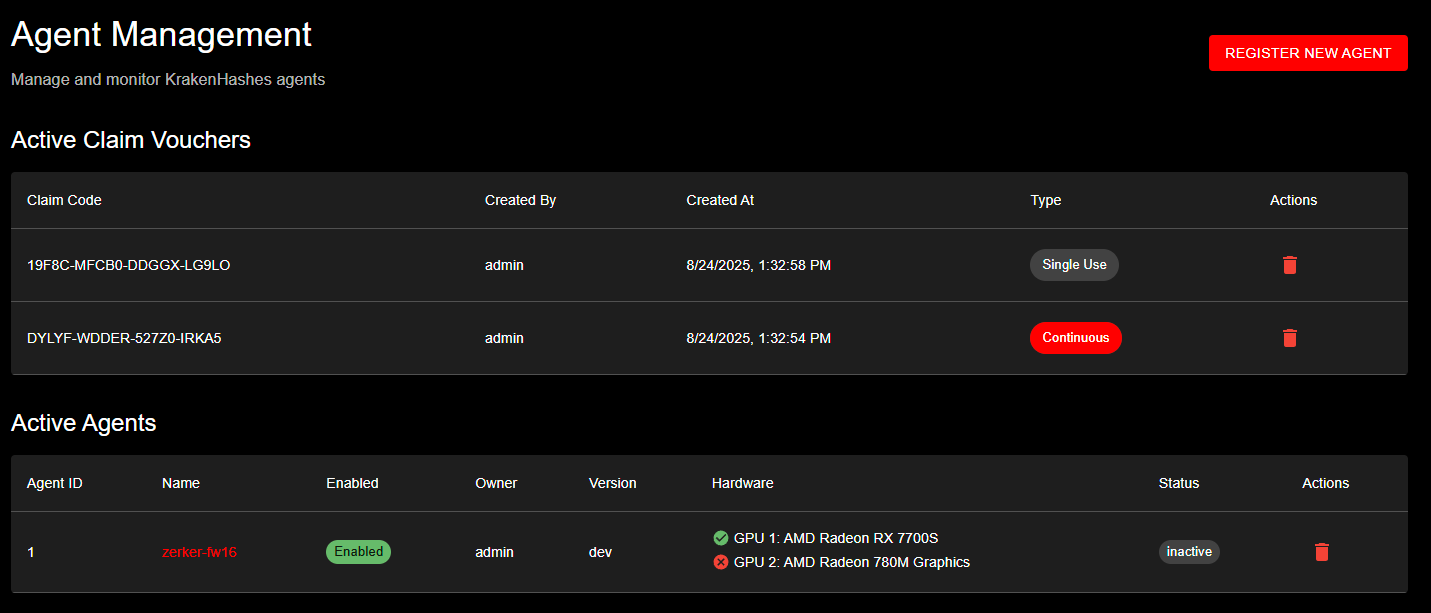 Agent Management interface showing active claim vouchers with different types and currently registered agents with their hardware configurations
Agent Management interface showing active claim vouchers with different types and currently registered agents with their hardware configurations
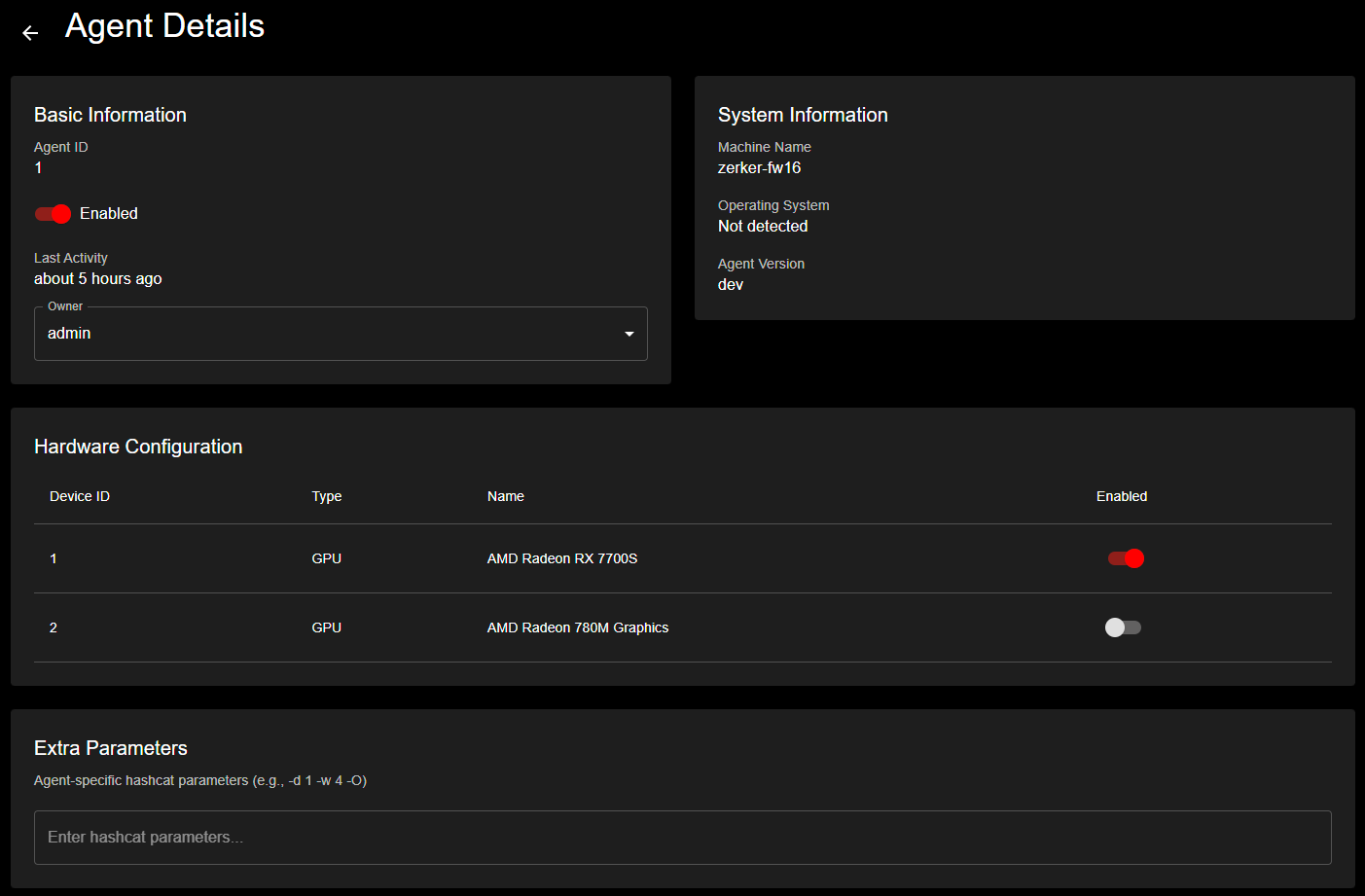 Detailed agent view displaying system information, hardware configuration, and GPU device management with enable/disable controls
Detailed agent view displaying system information, hardware configuration, and GPU device management with enable/disable controls
Managing Agent Connections¶
WebSocket Communication¶
Agents maintain persistent WebSocket connections for: - Real-time job assignments - Status updates - Crack result reporting - Heartbeat monitoring
Connection Parameters¶
# Environment variables for connection tuning
KH_WRITE_WAIT: "10s" # Write timeout
KH_PONG_WAIT: "60s" # Time to wait for pong response
KH_PING_PERIOD: "54s" # Ping interval (must be < pong wait)
Monitoring Connected Agents¶
- Dashboard View
- Real-time agent status on main dashboard
- Shows connected/disconnected agents
-
Current task assignments
-
Agent List Page
- Detailed view of all agents
- Filter by status, owner, or team
- Last heartbeat timestamps
Managing Agent Settings¶
// PUT /api/agents/{id}
{
"isEnabled": true,
"ownerId": "user-uuid",
"extraParameters": "--custom-charset1=?l?u?d"
}
Disabling/Enabling Agents¶
- Disabled agents remain connected but don't receive jobs
- Useful for maintenance or troubleshooting
- Preserves agent configuration and history
Monitoring Agent Health and Performance¶
Real-time Metrics¶
Agents report metrics every 30 seconds:
{
"cpu_usage": 45.2,
"memory_usage": 62.8,
"gpu_utilization": 98.5,
"gpu_temp": 72.0,
"gpu_metrics": {
"device_0": {
"temperature": 72,
"utilization": 98.5,
"memory_used": 8192,
"fan_speed": 85
}
}
}
Performance Monitoring Dashboard¶
- Agent Detail Page
- Historical performance graphs
- Temperature trends
- Utilization patterns
-
Hash rate performance
-
Metrics Time Ranges
- 1 hour (default)
- 24 hours
- 7 days
- 30 days
Device Management¶
Each agent can have multiple devices (GPUs):
// GET /api/agents/{id}/devices
[
{
"id": 1,
"device_index": 0,
"device_type": "GPU",
"device_name": "NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4090",
"is_enabled": true,
"capabilities": {
"compute_capability": "8.9",
"memory": 24576
}
}
]
Enabling/Disabling Devices¶
Agent Scheduling and Availability¶
Scheduling Overview¶
Agents support weekly scheduling to optimize resource usage and costs.
Configuring Agent Schedules¶
-
Enable Scheduling
-
Set Daily Schedules
Schedule Features¶
- UTC Storage: All times stored in UTC for consistency
- Timezone Display: Shown in user's local timezone
- Overnight Support: Schedules can span midnight
- Bulk Updates: Update entire week at once
Schedule Validation¶
- Start and end times must be different
- Day of week must be 0-6
- Times in HH:MM format
- Automatic handling of daylight saving time
Availability Considerations¶
When scheduling is enabled: - Agents only receive jobs during scheduled hours - Running jobs continue to completion - Agents remain connected outside schedule - Heartbeat monitoring continues
Hardware Capabilities and Benchmarks¶
Hardware Detection¶
Agents automatically detect:
{
"hardware": {
"cpus": [
{
"model": "AMD Ryzen 9 7950X",
"cores": 16,
"threads": 32,
"frequency": 4.5
}
],
"gpus": [
{
"vendor": "NVIDIA",
"model": "GeForce RTX 4090",
"memory": 24576,
"driver": "545.29.06"
}
]
}
}
Benchmark System¶
Agents can run benchmarks for different hash types:
-- Benchmark results stored per agent
agent_benchmarks (
agent_id,
attack_mode, -- 0=dictionary, 3=bruteforce, etc.
hash_type, -- 0=MD5, 1000=NTLM, etc.
speed, -- Hashes per second
created_at
)
Performance Metrics¶
Key metrics tracked: - Hash Rate: Speed for each hash type - GPU Temperature: Thermal monitoring - GPU Utilization: Processing efficiency - Memory Usage: VRAM consumption - Power Consumption: Wattage tracking
Consecutive Failure Tracking¶
Agents track consecutive task failures: - Increments on task failure - Resets on successful completion - Can trigger automatic disabling - Helps identify problematic agents
Agent Disconnection and Task Recovery¶
Understanding Disconnection Scenarios¶
KrakenHashes handles three distinct agent disconnection scenarios, each with specific recovery mechanisms:
1. Backend Restart (Planned or Unplanned)¶
When the backend server restarts while agents have running tasks:
What Happens: - Tasks transition to reconnect_pending state - Agents continue processing and cache crack results locally - Agent attempts reconnection with exponential backoff - Upon reconnection, agent reports current task status
Recovery Process: 1. Agent reconnects and sends current_task_status message 2. Backend validates the task belongs to this agent 3. Task transitions from reconnect_pending back to running 4. Cached crack results are processed 5. Job continues without losing progress
Grace Period: Configured via Admin Panel → Settings → Job Execution → Reconnect Grace Period (default: 5 minutes)
2. Graceful Agent Shutdown¶
When an agent is properly stopped (SIGTERM, Ctrl+C, or service stop):
What Happens: - Agent sends agent_shutdown notification to backend - Backend immediately marks task as pending for reassignment - No retry count increment (not a failure) - Task becomes available for other agents
Recovery Process: - Task is immediately available for reassignment - No grace period applies - Original agent can claim new tasks upon restart
3. Agent Crash or Network Failure¶
When an agent disconnects unexpectedly (crash, network loss, power failure):
What Happens: - Backend detects lost WebSocket connection - Task enters reconnect_pending state - Grace period timer starts
Recovery Process:
If agent reconnects within grace period: - Agent reports it has no running task - Backend marks task as pending for reassignment - Agent becomes available for new tasks
If grace period expires: - Task automatically transitions to pending - Available for any agent to claim - Retry count may increment based on configuration
Task State Transitions¶
running → reconnect_pending → running (agent reconnects with task)
running → reconnect_pending → pending (agent reconnects without task)
running → reconnect_pending → pending (grace period expires)
running → pending (graceful shutdown)
Monitoring Disconnection Events¶
Key Metrics to Watch¶
- Reconnection frequency: High frequency indicates network issues
- Grace period utilization: Tasks recovering vs. timing out
- Task reassignment rate: How often tasks move between agents
- Cached data volume: Amount of data agents cache during disconnections
Log Indicators¶
Backend logs to monitor:
INFO: Agent X: Task status - HasTask: true, TaskID: xxx
INFO: Task can be recovered [task_id=xxx, status=reconnect_pending]
INFO: Successfully recovered task
Agent logs to monitor:
INFO: Sending current task status to backend
INFO: Successfully sent current task status - HasTask: true
INFO: Connection state: disconnected
INFO: Reconnection attempt X - Waiting Ys before retry
Configuring Recovery Behavior¶
Reconnect Grace Period¶
Adjust based on your environment: - Stable networks: 3-5 minutes - Cloud environments: 5-10 minutes
- Unreliable networks: 10-15 minutes - Maintenance windows: 15-30 minutes
Best Practices¶
- Set grace period based on recovery time: Consider how long it takes to:
- Restart backend services
- Complete rolling updates
-
Recover from network outages
-
Monitor grace period effectiveness:
- Track successful recoveries vs. timeouts
- Adjust if seeing excessive reassignments
-
Consider agent network stability
-
Plan maintenance windows:
- Increase grace period before maintenance
- Notify users of extended recovery time
-
Monitor agent reconnections post-maintenance
-
Handle chronic disconnections:
- Identify agents with frequent disconnections
- Check network path and stability
- Consider dedicated network routes for critical agents
Troubleshooting Recovery Issues¶
Agent Not Recovering Task After Reconnection¶
Symptoms: Agent reconnects but task is reassigned
Common Causes: - Task ID mismatch between agent and backend - Database constraint violations (check backend logs) - Agent started fresh without cached state
Solutions: 1. Check agent has persistent storage for state 2. Verify task ID in agent and backend logs match 3. Review backend logs for "Failed to recover task" errors 4. Ensure database migrations are up to date
Tasks Stuck in Reconnect_Pending¶
Symptoms: Tasks remain in reconnect_pending after grace period
Common Causes: - Backend service not running task cleanup - Database lock preventing state transition - Incorrect grace period configuration
Solutions: 1. Verify job cleanup service is running 2. Check database for locks on job_tasks table 3. Manually transition stuck tasks if needed:
UPDATE job_tasks
SET status = 'pending', updated_at = NOW()
WHERE status = 'reconnect_pending'
AND updated_at < NOW() - INTERVAL '10 minutes';
Excessive Task Reassignments¶
Symptoms: Tasks frequently moving between agents
Common Causes: - Grace period too short - Network instability - Agents crashing frequently
Solutions: 1. Increase reconnect grace period 2. Investigate network stability 3. Check agent system resources and logs 4. Consider agent health checks
Troubleshooting Agent Issues¶
Common Connection Issues¶
- Agent Won't Connect
- Check TLS certificates are valid
- Verify API key hasn't expired
- Ensure firewall allows WebSocket (port 8443)
-
Check agent logs for detailed errors
-
Frequent Disconnections
- Review ping/pong timeout settings
- Check network stability
- Monitor agent system resources
- Verify no proxy interference
Authentication Problems¶
-
Invalid API Key
-
Certificate Issues
- Check certificate expiration
- Verify CA certificate is trusted
- Ensure certificate matches server hostname
Performance Issues¶
- Low Hash Rates
- Check GPU driver versions
- Monitor thermal throttling
- Verify power settings
-
Review extra parameters
-
High Failure Rate
- Check hashcat binary compatibility
- Verify file synchronization
- Review job parameters
- Monitor system stability
Debugging Tools¶
-
Agent Logs
-
Server-side Monitoring
-
WebSocket Messages
- Enable debug logging for detailed messages
- Monitor heartbeat intervals
- Check message acknowledgments
Recovery Procedures¶
-
Reset Agent State
-
Force Reconnection
- Restart agent service
- Clear local cache
-
Verify network connectivity
-
Complete Re-registration
- Generate new claim code
- Remove agent from database
- Perform fresh registration
Monitoring Best Practices¶
- Set Up Alerts
- Agent offline > 5 minutes
- Consecutive failures > 3
- Temperature > 85°C
-
Low hash rates
-
Regular Maintenance
- Update agent software
- Clean GPU fans
- Check thermal paste
-
Update drivers
-
Capacity Planning
- Monitor job queue depth
- Track agent utilization
- Plan for peak loads
- Consider scheduling optimization
Advanced Topics¶
Agent Clustering¶
- Group agents by capability
- Assign specialized workloads
- Balance load across regions
- Implement failover strategies
Security Hardening¶
- Rotate API keys periodically
- Implement IP whitelisting
- Use dedicated agent VLANs
- Monitor for anomalous behavior
Integration Points¶
- Export metrics to monitoring systems
- Webhook notifications for events
- API automation for scaling
- Custom scheduling algorithms
Conclusion¶
Effective agent management is crucial for maintaining a high-performance distributed cracking system. Regular monitoring, proper scheduling, and proactive troubleshooting ensure optimal resource utilization and job completion rates.
For additional support or advanced configurations, consult the system administrator documentation or contact the development team.